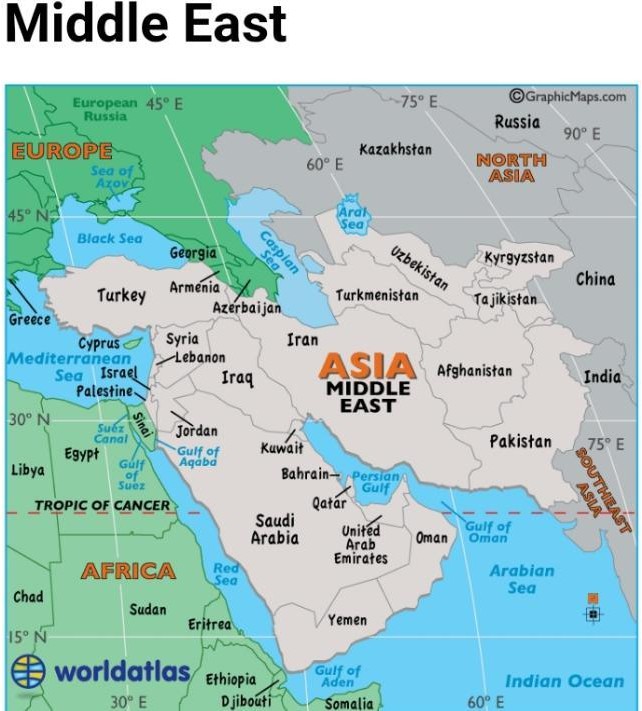
Peace vanished as Middle East has remained one of the most unstable regions for decades, shaped by historical, political, and religious complexities. The roots of ongoing tensions trace back to the collapse of the Ottoman Empire and the imposition of artificial borders by colonial powers after World War I. In addition to this, the discovery of oil, the establishment of Israel in 1948, and foreign interventions have deepened divisions.
The region is entangled in multiple conflicts, including the Israel-Palestine issue, the Syrian civil war, Iran-Saudi rivalry, and proxy wars in Yemen and Lebanon. While numerous peace initiatives — such as the Oslo Accords, UN Resolutions, and Abraham Accords (U.S. State Department) — have been attempted, a lasting solution remains out of reach.
Conflict Root Causes
Territorial claims of Palestine and Israel are the main conflicts in the Middle East. This has led to violence that escalates at different points. 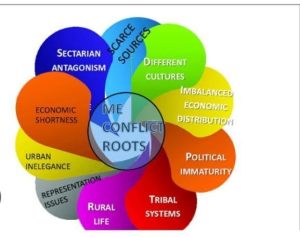 The sectarian division of Sunni-Shia — a hypothetical divide between Saudi Arabia and Iran — intensifies this violence. Many countries often face one another in proxy wars, like Syria or Yemen, directly or indirectly supporting adversaries.
The sectarian division of Sunni-Shia — a hypothetical divide between Saudi Arabia and Iran — intensifies this violence. Many countries often face one another in proxy wars, like Syria or Yemen, directly or indirectly supporting adversaries.
The rise of extremist groups (ISIS) has led to chaos (BBC News). Finally, the role of foreign countries like the USA, Russia, and China only adds to matters because it is very uncommon for them to advocate for a resolution of the violence, and it is even much less frequent for them to favor or adhere to any similar agenda. Foreign influence and regional interests contribute to the instability of the region and a cycle of violence and distrust among parties.
Key Players and Their Interests
The Middle East conflict is shaped by the competing interests of powerful regional and global players. Israel prioritizes security, regional recognition, and maintaining control over disputed territories. Palestinians demand an independent state, equal rights, and an end to occupation.
Iran aims to expand its influence through proxy groups like Hezbollah, often opposing Saudi Arabia, which seeks regional dominance and sees Iran as a major threat. On the global stage, the United States strongly backs Israel and Saudi Arabia, motivated by security alliances, oil interests, and geopolitical control. Russia supports Iran and Syria to counterbalance U.S. influence and maintain access to strategic ports. The European Union encourages peaceful dialogue but holds limited sway.
Recent agreements like the Abraham Accords, which normalize ties between Israel and some Arab states, show shifting alliances (U.S. State Department); yet deep-rooted rivalries and mistrust continue to drive instability.
Humanitarian Impact and Civilian Suffering
Since October 2023, over 2 million Gazans have been displaced — many more than once — due to relentless conflict and ceasefire collapses (UN OCHA). Across the MENA region, nearly 56 million people require humanitarian aid, including 16 million internally displaced individuals.
 Civilian casualties are devastating, with 48,000 to 56,000 reported deaths in Gaza, a significant number being women and children. Psychological trauma, especially among children, is severe. Over 90% of Gaza’s hospitals are damaged or shut down, facing critical shortages of medicine and supplies. Hundreds of schools lie in ruins, disrupting education.
Civilian casualties are devastating, with 48,000 to 56,000 reported deaths in Gaza, a significant number being women and children. Psychological trauma, especially among children, is severe. Over 90% of Gaza’s hospitals are damaged or shut down, facing critical shortages of medicine and supplies. Hundreds of schools lie in ruins, disrupting education.
Widespread communication blackouts hinder rescue and aid efforts. Food insecurity is acute — every one of Gaza’s 2.1 million residents is affected, with 500,000 at risk of famine (WFP). Relief agencies like UNRWA, UNICEF, and WFP continue to provide aid despite access and safety challenges (UNRWA).
Role of International Organizations in Mediating Peace
International organizations play a key role in promoting global peace and resolving conflicts. The United Nations (UN), African Union (AU), and European Union (EU) often act as neutral parties to bring conflicting sides to the table. They offer peacekeeping missions, mediation, and dialogue platforms.
For example, the UN has helped reduce tensions in countries like Sudan and Afghanistan through diplomatic efforts and peacekeeping forces. These organizations also provide humanitarian aid, monitor ceasefires, and support rebuilding processes after war. Their global presence, legal frameworks, and experienced teams make them valuable for long-term peace.
Although not always successful, their efforts create hope and stability in conflict zones. Overall, international organizations are essential in reducing violence and building trust between nations.
Diplomatic and Political Solutions
Despite multiple initiatives, the region remains divided due to great power competition and complex internal dynamics. To bring peace, it is pertinent that foreign powers cease their interference in the region.
 While the Oslo Accords ultimately failed, agreements like the 2020 Abraham Accords and the 2023 Saudi-Iran rapprochement mediated by China are constructive steps (Al Jazeera). Strengthening the role of international and regional organizations is vital to promoting peace through inclusive multilateral diplomacy.
While the Oslo Accords ultimately failed, agreements like the 2020 Abraham Accords and the 2023 Saudi-Iran rapprochement mediated by China are constructive steps (Al Jazeera). Strengthening the role of international and regional organizations is vital to promoting peace through inclusive multilateral diplomacy.
Also, the UNGA’s 2025 reaffirmation of the two-state solution and condemnation of Israel’s illegal occupation mark a significant step forward (UN News). For lasting peace and stability, genuine regional and global cooperation, reduced foreign intervention, and mediation by superpowers are essential.
Challenges to Implementing Peace
Peace in the Middle East remains elusive due to complex and interlinked challenges. Historical grievances, notably the unresolved Israeli-Palestinian conflict, continue to ignite violence. Ethnic and sectarian divisions, foreign interventions, and proxy wars — particularly in Syria, Yemen, and Libya — exacerbate instability.
Weak political institutions, authoritarian regimes, and corruption hinder diplomatic progress. Extremism, terrorism, and arms proliferation further destabilize the region. Geopolitical rivalries, especially between Iran and Saudi Arabia, obstruct regional cooperation. Socioeconomic inequalities and youth unemployment deepen public resentment.
Peace efforts often collapse due to mistrust, biased mediators, and lack of enforcement mechanisms. In order to stabilize the Middle East, it requires inclusive dialogue, international neutrality, economic investment, and respect for sovereignty. Strengthening regional organizations and promoting education can address root causes of conflict. Only a multilateral, locally-driven approach offers hope for lasting peace.
Call to action
The Middle East has suffered for generations due to unresolved political conflicts, historical wounds, and  constant foreign involvement. While leaders have signed treaties and held peace talks, the region continues to bleed, and innocent people — especially women and children — keep suffering silently. Still, peace is not impossible. If nations put people before power, and listen before acting, progress can happen. Education, youth involvement, and fair dialogue can reshape the future. No region deserves to live in fear or hunger. A peaceful Middle East will not come overnight, but with honest cooperation, mutual respect, and a focus on justice, is within its reach. Real peace begins when humanity comes first — not politics.
constant foreign involvement. While leaders have signed treaties and held peace talks, the region continues to bleed, and innocent people — especially women and children — keep suffering silently. Still, peace is not impossible. If nations put people before power, and listen before acting, progress can happen. Education, youth involvement, and fair dialogue can reshape the future. No region deserves to live in fear or hunger. A peaceful Middle East will not come overnight, but with honest cooperation, mutual respect, and a focus on justice, is within its reach. Real peace begins when humanity comes first — not politics.
Recommendations
- Start more youth programs to teach peace, leadership, and
- Support stronger UN peacekeeping teams to protect people during
- Promote honest media and education to stop hate and spread
- Encourage neighboring countries to work together on trade, schools, and health.
By PNP Inters – Sobia Hamid, Amreena, Hira Imtiaz, Syeda Tatheer Zahra, Muhammad Huzaifa, Qurat-ul-Ain, Muhammad Taha, Muhammad Akram
This post has been submitted by our group of interns. PNP Internship Program is an exciting career opportunity for Pakistani university students to get hands-on valuable experience required in national and international job market.
In order to ensure transparency, accuracy and accountability to our readership, please report whenever any error found or need to clarify /correct the post.