“The large-scale humanitarian and protection crisis shows no sign of abating,” said Matthias Schmale, the UN Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Nigeria. “An estimated 2.4 million people are in acute need – impacted by conflict, disaster and disease – and require urgent support.”
Warnings of catastrophe
The “ticking time bomb” of child malnutrition is escalating in Nigeria’s northeast, with the number of children suffering from acute malnutrition projected to increase to two million in 2023, up from 1.74 million last year, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) said.
Already high levels of severe acute malnutrition are projected to more than double from 2022 to a projected 697,000 this year.
“Women and girls are the hardest hit,” said Mr. Schmale. “Over 80 per cent of people in need of humanitarian assistance across Borno, Adamawa and Yobe states are women and children. They face increased risks of violence, abduction, rape and abuse.”
Without urgent action, 4,000 people in Bama, Borno state, are expected to face such catastrophic conditions as starvation, death, destitution, and extremely critical acute malnutrition levels become prevalent, OCHA said.
Sudden attacks on civilians
During the devastating ongoing 13-year-long armed conflict, children, girls, women and people with disabilities have been the most affected. They require additional attention through enhanced access to protection and basic health, nutrition, water, sanitation, hygiene, and learning services.
Meanwhile, two million people have been displaced due to conflict, many of them experiencing daily threats to their health and safety.
Non-State armed groups continue to stage unpredictable attacks on civilians and civilian infrastructure. In addition, the recent closure of camps for internally displaced persons are leading to new vulnerabilities.
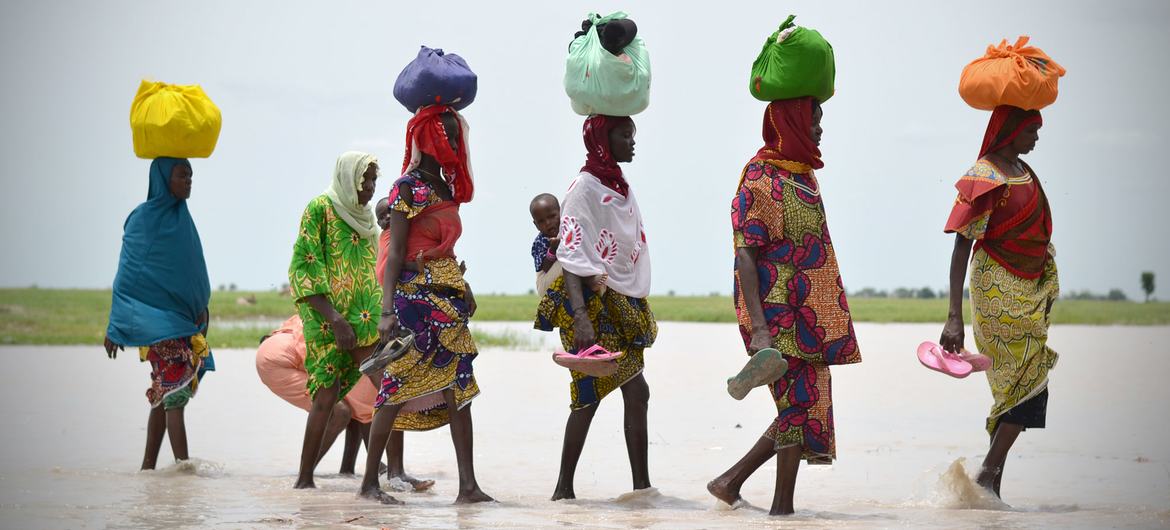

Women walk across a body of water in Rann, Borno State, Nigeria.
Calls to prevent atrocity crimes
In 2022, the UN provided emergency assistance to almost 5 million people in Nigeria in response to these and other crises, including severe malnutrition in the northwest and the worst flooding Nigeria has seen in a decade.
Earlier this month, the UN Special Adviser on the Prevention of Genocide Alice Nderitu raised concerns about a worsening security situation, calling for urgent action to address conflicts and prevent atrocity crimes.
The 2023 plan prioritizes life-saving needs while working to reduce vulnerabilities and build resilience. Contributions can be made to the Humanitarian Response Plan through the Financial Tracking Service, Nigeria Humanitarian Fund, or the Central Emergency Response Fund.